 GFC Blog:
GFC Blog:
by Media Relations Specialist Stasia Kelly
It’s summertime in Georgia…do you know where your energy dollars are going? Chances are, the cost of cooling your home has risen, with no obvious way to stop the bleeding other than sweating it out. Unless, that is, you take time this month to evaluate your home’s surroundings for places to plant trees that will help reduce energy costs in the years ahead.
Simply put, it takes a lot of energy to cool our homes! They absorb the sun’s rays, converting them to heat, and then radiating that heat back into our living spaces. The heat from roofs, walls, sidewalks, driveways, roads, and parking lots raises homes and offices’ temperatures to uncomfortable levels. While insulation is better today than in the past, homes, and offices devour more than 18 percent of our summer energy use for cooling indoor air.
 Homeowners and energy utilities are rediscovering tree planting as a time-tested method for reducing energy use. Research has shown roofs, windows, and air conditioners shaded by trees help reduce energy usage by up to 20 percent. Trees’ leaves are valuable tools that shade the heat-absorbing surfaces of our homes. As the sun’s rays strike the leaves, the rays are blocked and absorbed. This is particularly beneficial between the daylight hours of 11 a.m. and 6 p.m., when the sun’s energy has the highest impact on our homes. Placing the proper tree species on the east, south and west sides of homes can significantly impact cooling bills and quickly pay back the installation and maintenance costs. Shaded surfaces also need to be painted less frequently, thereby decreasing overall maintenance costs.
Homeowners and energy utilities are rediscovering tree planting as a time-tested method for reducing energy use. Research has shown roofs, windows, and air conditioners shaded by trees help reduce energy usage by up to 20 percent. Trees’ leaves are valuable tools that shade the heat-absorbing surfaces of our homes. As the sun’s rays strike the leaves, the rays are blocked and absorbed. This is particularly beneficial between the daylight hours of 11 a.m. and 6 p.m., when the sun’s energy has the highest impact on our homes. Placing the proper tree species on the east, south and west sides of homes can significantly impact cooling bills and quickly pay back the installation and maintenance costs. Shaded surfaces also need to be painted less frequently, thereby decreasing overall maintenance costs.
It’s important in summer to care for trees that are already established. Nothing replaces a large shade tree for immediate impact, so be sure to follow a regular watering schedule when rainfall patterns are irregular.
Now is the time to make a plan for Georgia’s ideal tree planting season, which runs from November until March. Here’s what to look for.

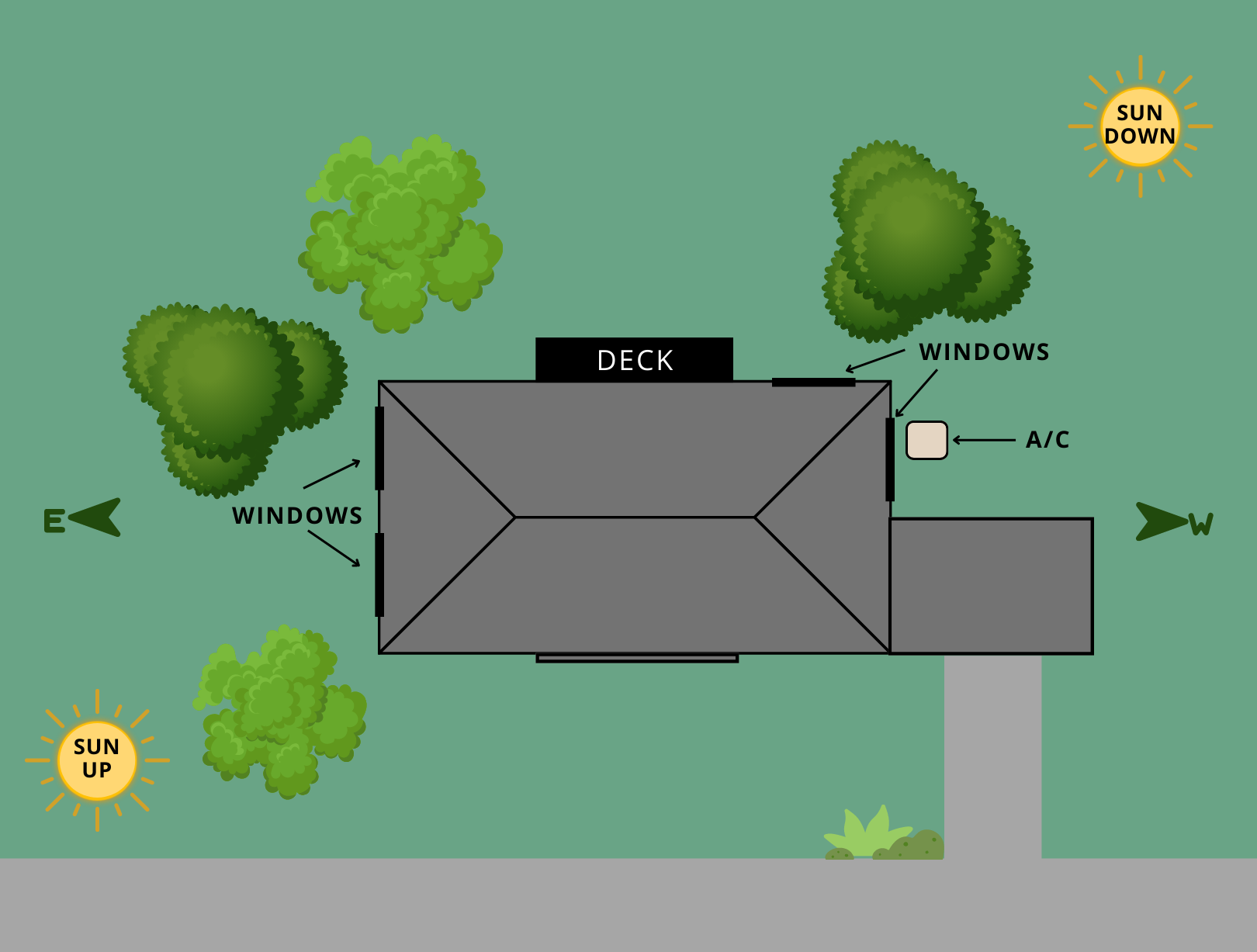
- Determine where the sun rises and sets with respect to your home’s location.
- Figure out which areas (windows, walls, doors, air conditioning units or decks) receive the most hours of direct sun and indirect sun (reflected sun).
- Given the sun’s angle at different parts of the day, determine where the shade needs to be to most effectively block the sun.
- Determine how much space is available for the tree’s root system. A large tree requires about 600 square feet of soil surface area and a small tree needs 100-200 square feet.
- Be sure the larger trees aren’t planted too close to the house – at least 15 to 20 feet away is needed to allow for future growth. Also, remember to not use evergreen trees on the south and west sides of the house.
Planting deciduous trees in these locations allow the sun’s warming rays to reach the house through the trees’ branches in winter.
If you are unable to plant trees everywhere you need or want them, the following list can help you prioritize desired locations based on their energy-saving potential:
- Air conditioning units on the south or west side of the home
- West and southwest facing windows and doorways
- East and southeast-facing windows
- West and southwest facing wood-sided walls
- Any deck areas that reflect light to the interior of the home.

Planting trees properly is critical to the long-term success of your energy conservation project and can raise your property value by up to five percent. Safety precautions and planting tips can be found at gatrees.org/resources and enter “tree planting” in the Search bar and on our YouTube Channel,
